Extractive Industry
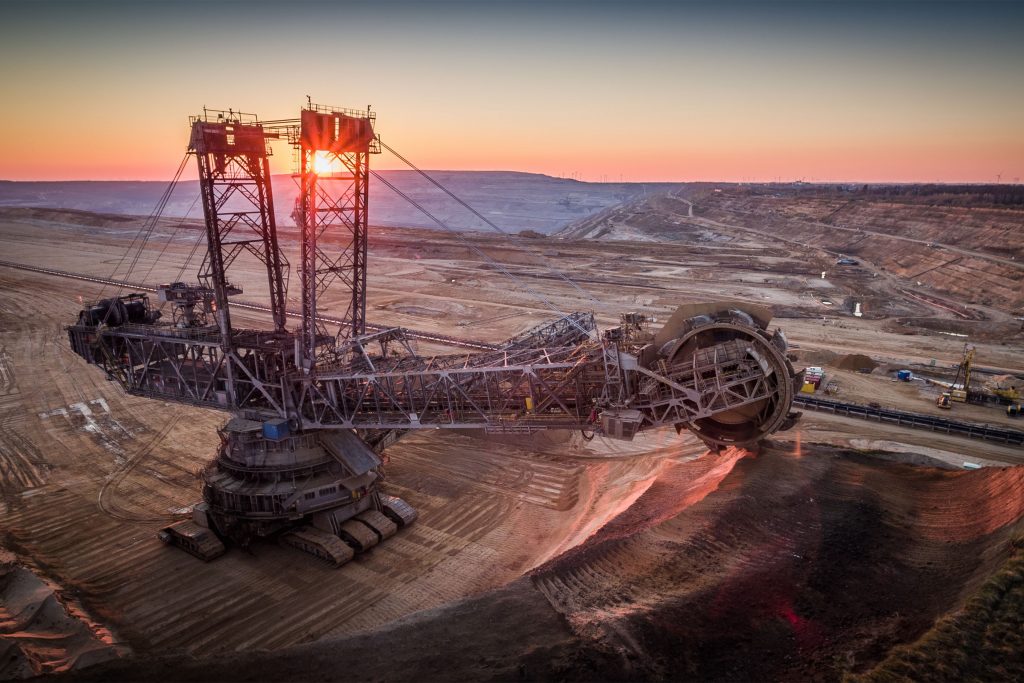
Mining
- Underground (Digging down into the earth, creating tunnels and shafts to reach the deposits of resources)
- Surface (Open Pit; digging out rocks while Strip; Extraction of shallow bedded deposits)
- Placer (Normally formed by weathering via water or wind e.g. panning for gold)
- In Situ (Pumping of chemicals underground to dissolve resource-containing ore then pumping pregnant solution back to surface leads to process for recovery of resources)

Minerals
- Native Elements. e.g. Gold, Silver, Mercury, graphite, diamond.
- Oxides. e.g. corundum (incl. sapphire), hematite, spinel.
- Sulfides. e.g. Pyrite, galena, sphalerite.
- Sulfates. e.g. Baryte, gypsum.
- Carbonates. e.g. Calcite, magnesite, dolomite.
- Phosphates. e.g. Apatite, monazite.
- Halides. e.g. Fluorite, halite (rock salt).
- Silicates (most common)
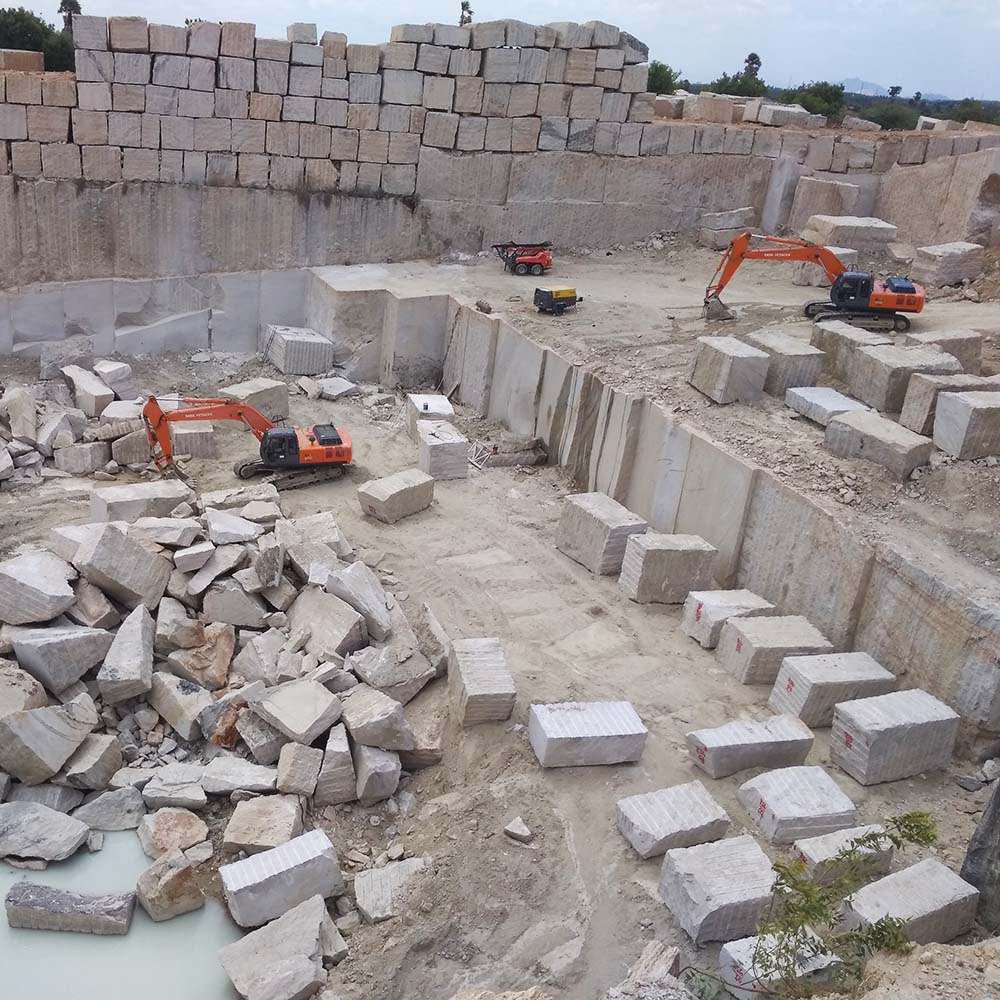
Quarrying
- Hard Rocks / Stones
- Natural Sand and Gravel
- Sandstone
- Limestone
- Marine/Ocean

